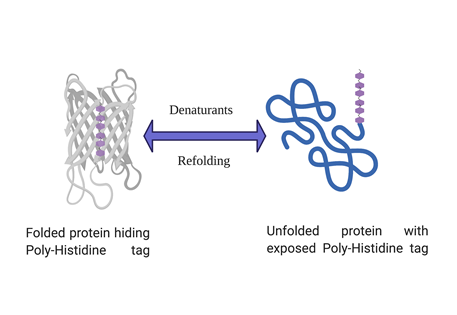
Poly-histidine tagged proteins account for more than 90% of routine recombinant protein expression and purification. Histidine tag has many advantages over other affinity tags such as small size, high affinity for binding to IMAC resins (Immobilized metal affinity chromatography) and allows one step purification of recombinant protein. But sometimes a histidine tagged protein doesn’t bind to the affinity column and evades it’s capture and subsequent purification. Although such instances are not very common but can be very frustrating whenever they happen. However, there are ways to troubleshoot if such a problem arises and the solutions are discussed below in a step by step manner.
His-tagged protein expressing but not binding your Ni-NTA column?
Topics: Protein Purification, Western Blotting, Protein Electrophoresis, Sample Clean Up, Protein Concentration, Protein Fractionation, Protein Labeling, Protein Extraction, Protein Detection
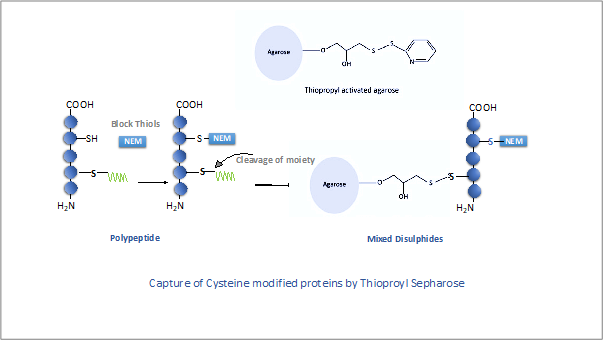
Cysteine is one of the most reactive amino acid residue owing to the thiol (-SH) group, thiols can serve as an electron donor in different reactions. Cysteine thiols can form part of catalytic centre and can frequently participate in enzymatic reactions, not just that, cysteine thiols can also undergo a variety of covalent post-translational modifications (PTMs) and formation of disulphide bonds. The thiol modifications can act as important mediators of redox signalling and protein function regulation.
Topics: Protein Purification, Protein Electrophoresis, Sample Clean Up, Protein Extraction
What is the Link between Protein Folding and Prion Disease?
Prion diseases (also referred to as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, or TSEs) are a group of progressive, untreatable, and fatal neurodegenerative conditions affecting both humans and animals. Generally, these conditions are characterized by long incubation periods (usually between 5 to 20 years), disruption in the normal tissue structure (resulting in holes and vacuole formation in the neurons), and the absence of an inflammatory response.
Topics: Protein Purification, Molecular Biology, Western Blotting, Protein Electrophoresis, Cytotoxicity Assays, Sample Clean Up, Protein Concentration, Protein Fractionation, Protein Labeling, Protein Extraction, Buffers & Chemicals
Exploring the Genetic Causes of ALS (Lou Gehrig's Disease)
Despite the advances in modern medicine, no one knows for sure what causes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also called Lou Gehrig’s disease. Scientists can only theorize and speculate as to what causes it, but they still don’t have a conclusive answer to this question.
Topics: Protein Purification, Western Blotting, Assay Development (ELISA), Sample Clean Up, Protein Concentration, Protein Extraction, Protein Detection