Topics: Protein Purification, Western Blotting, Protein Electrophoresis, Protein Estimation, Sample Clean Up, Protein Concentration, Protein Fractionation, Protein Extraction, Buffers & Chemicals, Protein Detection
Proteinase K is a serine protease, the presence of a catalytic triad characterizes serine proteases, the catalytic triad is a cluster of three amino acids that make the catalytic center and consists of serine, aspartic acid, and histidine amino acids, which can often vary but all of these enzymes have a nucleophile serine and the same catalytic mechanism. Proteinase K has a catalytic triad consisting of Ser 224, His 69, and Asp 39. The substrate recognition sites are made up of peptide chains, 99-104 and 132-136.
Topics: Protein Purification, Molecular Biology
Detergents are amphipathic compounds with a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail and a polar, hydrophilic head group. Due to these structural features detergents tend to aggregate into structures called micelles at high enough concentration; arranging themselves with their hydrophobic tails pointed inwards and their hydrophilic heads pointed outwards. Detergents come in three types: ionic (cationic and anionic) and non-ionic. Non-ionic detergents aren’t generally used for gel electrophoresis due to their limited ability to break non-covalent interactions between protein residues and inability to impart a uniform charge onto the protein. Ionic detergents (typically anionic SDS) are used for gel electrophoresis as they are highly useful for protein solubilization, linearization and for establishing a uniform charge in preparation for gel electrophoresis.
Topics: Protein Purification, Western Blotting, Protein Estimation, Detergents, Sample Clean Up, Protein Concentration, Protein Fractionation, Protein Labeling, Protein Extraction, Protein Detection
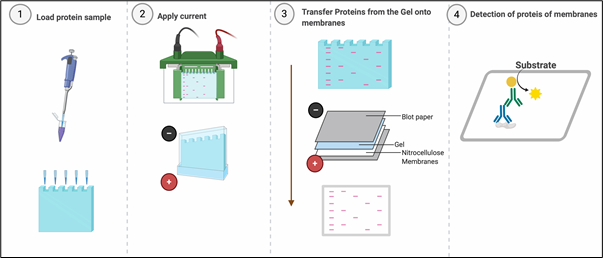
Western blotting or immunoblotting is an indispensable technique, almost every published paper in area of molecular cell biology uses western blotting for detecting specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or cell lysates. Western blotting combines resolving power of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) or SDS-PAGE and specificity of antibodies to detect target proteins. Proteins are resolved on the basis of their molecular weight in SDS-PAGE and transferred from the polyacrylamide gel onto the membranes (Nitrocellulose or PVDF), which creates an exact replica of the protein separation pattern on the membrane. After transferring the proteins to the membrane, the membrane needs ‘blocking’ to ‘block’ non-specific binding sites on the surface of the membrane. Blocking is usually performed with Bovine Serum Albumin, Skimmed milk or purified milk Casein.
Topics: Protein Purification, Western Blotting, Protein Electrophoresis, Protein Estimation, Sample Clean Up, Protease Inhibitors, Protein Extraction, Protein Detection