Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) remains a cornerstone method for protein purification, valued for its ability to deliver high-purity samples with minimal loss of biological activity. From structural analysis to functional studies and therapeutic development, the purity of protein preparations directly impacts experimental outcomes.
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): A Critical Tool for Protein Purification
Topics: Protein Purification, Size exclusion chromatography,, Chromatographic resins, Gel filtration chromatography
Magnetic bead technology has emerged as a linchpin, offering researchers a robust and flexible
tool for a wide range of applications—from isolating specific cell populations to streamlining
immunoprecipitation protocols. Magnetic beads are used to immobilize molecules (e.g., proteins,
enzymes, peptides, antibodies, nucleic acids) on a solid phase, thereby separating them from the
lysate. When the sample is added to the beads and a magnetic field is applied to the mixture, the
target molecule binds to the beads, allowing it to be separated from the rest. The beads are then
washed to remove impurities, and the target molecule is eluted using an appropriate buffer.
Topics: Protein Purification, Cell separation, Nucleic acid purification, Immunoprecipitation, Next-generation sequencing (NGS), PCR/qPCR
Protein Purification
When investigating a particular protein of interest, the first step is to separate it from the non-protein components and from all the other proteins in the complex sample mixture (cell, tissues, or whole organisms) by exploiting differences in size, physical and chemical properties, binding affinity, and biological activities of individual proteins.
Basically, protein purification allows researchers to identify and examine the properties of the protein of interest, including its structure, function, and interactions. When classified according to purpose, protein purification can either be preparative or analytical.
Topics: Protein Purification
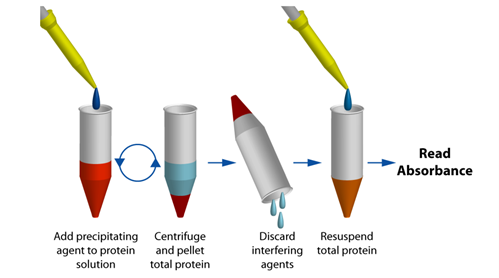
Protein Quantitation in the Presence of Reducing Agents and Detergents with UPPA™
Topics: Protein Purification