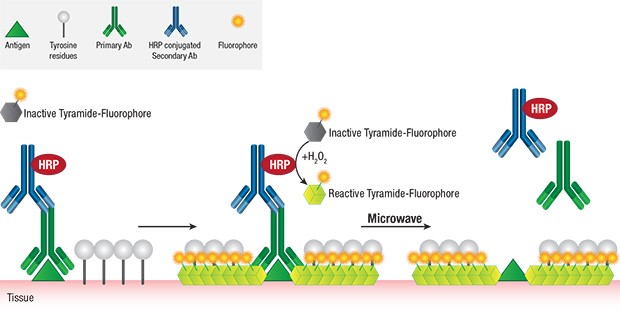
Diagnostic field has been a progressing area with multiple tools identified for specific proteins detection and their quantification. Diagnosis in pathology or clinical set up has multiple numbers of challenges owing to time constraint, increasing numerosity and complexity of the detection methods, less amount of sample and so on, which is essentially important for disease identification, refining of pathological interventions and development of an appropriate prognosis. Pathological detection is most commonly performed by utilizing antibody-antigen interactions (by deposition of a visible product or fluorochrome based detection). The standard approach is to perform one or two protein detection at a time on the serial sections, which is cumbersome if the sample availability is low and the proteins to be detected are high in number. More often fluorescent reporters are used for both detection and quantitation methods such as image cytometry, flow cytometry, confocal microscopy, etc. using live tissue or slightly fixed tissue, while the conventional immunohistochemistry involves heavily fixed tissue sections. Recently, in the wake of developing user-friendly and multiple assays on formalin fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) specimens are being developed and gaining ground, known as Multiplexing or multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC), which allows use of more than three different stains performed on one sample/ slide.
Protein Solubility & Refolding Active Proteins from Inclusion Bodies
Over expression of recombinant protein in bacteria can lead to the accumulation of insoluble protein, which aggregates and is sequestered to inclusion bodies. Slow growth rate and low temperatures during protein expression will help in solubility of many over expressed proteins, however some proteins still form Inclusion Bodies. Inclusion Bodies are pure proteins aggregated in bacterial cytoplasm, but sometimes can be formed in periplasm. Though the process of purification is tedious, we can get pure active protein by using various purification steps. Utmost care to be taken during Inclusion Bodies purification as the process is harsh on delicate proteins and may result in the loss of protein activity.
Topics: Protein Extraction
The Sandwich ELISA: Process and Practical Applications
The Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is one of the most efficient laboratory procedures used in detecting the presence and measuring the concentration of a target antigen in a completely unknown sample. Its superior sensitivity and extremely robust nature makes it a great diagnostic tool for medical purposes and is especially useful in identifying potential food allergens and/or testing for certain drugs.
Topics: Assay Development (ELISA)
How to Improve Spot Resolution During 2D-Electrophoresis
While several protein separation technologies have been developed in recent years, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis remains one of the most popular techniques used in the field of proteomics. This is not surprising since 2D PAGE is routinely used to accurately analyze the individual components of even the most complex proteins, and can simultaneously resolve more than 5000 proteins (depending on the gel size used).
Topics: Protein Electrophoresis