Affinity purification, also called affinity chromatography, is a laboratory technique used for purifying protein or protein complexes within a biochemical mixture. Unlike other chromatography-based purification methods which separate molecules based on size (i.e., gel filtration or size-exclusion chromatography) or strength of ionic interaction with a solid phase material (i.e., ion exchange chromatography), affinity purification works by manipulating certain molecular properties and specific binding interactions between molecules to purify the protein of interest.
The Basics of Affinity Purification/Affinity Chromatography
Topics: Protein Purification
Restriction Enzyme Analysis: How to Make the Cut
A restriction enzyme (restriction endonuclease) is a special enzyme that recognizes a specific sequence of nucleotides and cleaves DNA at that specific site (restriction site or target sequence). These enzymes, which are usually found in bacteria and other prokaryotes, are considered as one of the most important tools in recombinant DNA technology since they can easily cut DNA into fragments and/or join DNA molecules from different genomes so researchers can identify and characterize genes and examine gene expression and regulation.
Topics: Molecular Biology
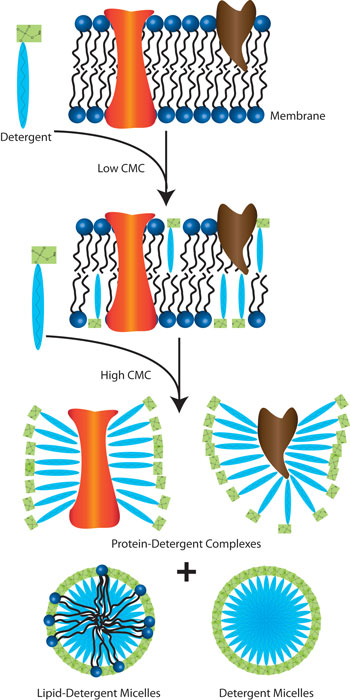
Proteomic Grade Detergents: Why you should use them
Detergents play an extremely critical role in cell lysis and protein extraction. With their unique amphipathic nature (they possess a polar head group on one end that interacts with the hydrogen bonds of water molecules and a long hydrophobic carbon tail which aggregate to form micelles on the other end), this class of molecules can easily disrupt the hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions between biological molecules in aqueous solutions.
Topics: Detergents
Exosome isolation by centrifugation, filtration, immunoaffinity & more
Earlier designated as the "garbage bags" used by the biological systems to remove unnecessary biomolecules of the cells, Exosomes, have recently gained popularity as secreted vesicles pivotal for intracellular and intercellular information transfer. Studies have shown the presence of essential RNA and protein cargos in these small vesicles (30-150 nm). The interest in exosome studies have exponentially grown as they can be manoeuvred as minimally diagnostic tools in order to understand biological functions. Proteomics of exosomes are considered the biological fingerprints as they replicate the properties of the parental cell from where they are originated. As a mobile container of vital biomolecules (specialized proteins and RNAs) exosomes are crucial for antigen- presentation, cell-cell communication, waste management, translocation of biomolecules and coagulation.
Topics: Protein Extraction