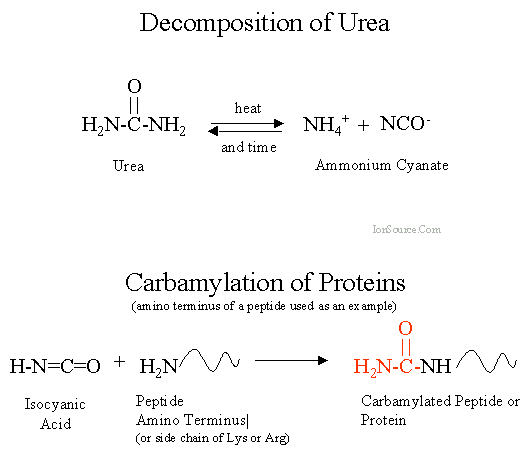
When it comes to solubilizing and denaturing proteins prior to isoelectric focusing and 2-D gel electrophoresis, most researchers choose urea. This is not surprising since this mild chaotropic agent can completely disrupt the interactions between protein molecules and increase the efficiency of protease activity in protein digestion while effectively preventing proteins from aggregating and/or precipitating. In addition, urea is also used for renaturing proteins from previously denatured samples.
Preventing Carbamylation When Using Urea as a Protein Solubilization Buffer
Topics: Protein Extraction
8 Factors to Consider when Selecting a Protein Cross-linker
Protein cross-linking reagents, fondly called “cross-linkers” by researchers, are molecules with two or more reactive ends that can attach themselves to specific functional groups (e.g., primary amines, carboxyls, sulfhydryls, carbohydrates, and carboxylic acids) on proteins and other biomolecules via a covalent bond.
Topics: Cross-Linkers
BCA or Bradford Protein Assay: Choosing Between the Two
Which protein assay should you choose for your experiment – the BCA (Bicinchoninic Acid) protein assay or the Bradford protein assay? Since there is practically not a single protein assay method that is perfectly specific to particular proteins or sensitive to all protein types, your success will ultimately depend on three important factors:
Topics: Protein Estimation
As a functional unit of a living entity, cells are very complicated and consist of exceptionally high number of biomolecules with completely different physical and chemical properties. The complexity of the biomolecules profile is even more intricately woven depending upon their subcellular location. With the limited resolution of the separation and localization technologies, it is imperative to employ fractionation methods for protein profiling and expression analysis. Even the lesser abundant proteins can be analysed if screened after prefractionation. Sensitive and accurately fractionated samples help in convolution of methods such as mass spectrometry or in-vitro analysis for the detection of proteins at the level of organelles or transportation compartments.
Topics: Protein Fractionation