In 1994, the vision of one man became a reality as Geno Technology became an incorporated company and began offering its first invention, the GeneCAPSULE. The inventor and current CEO of the company is Dr. Aftab Alam, who in the infancy of the company wore every hat imaginable, including inventor, designer, manufacturer, marketer, sales rep and customer service.
The Protein Man

Recent Posts
Topics: Service
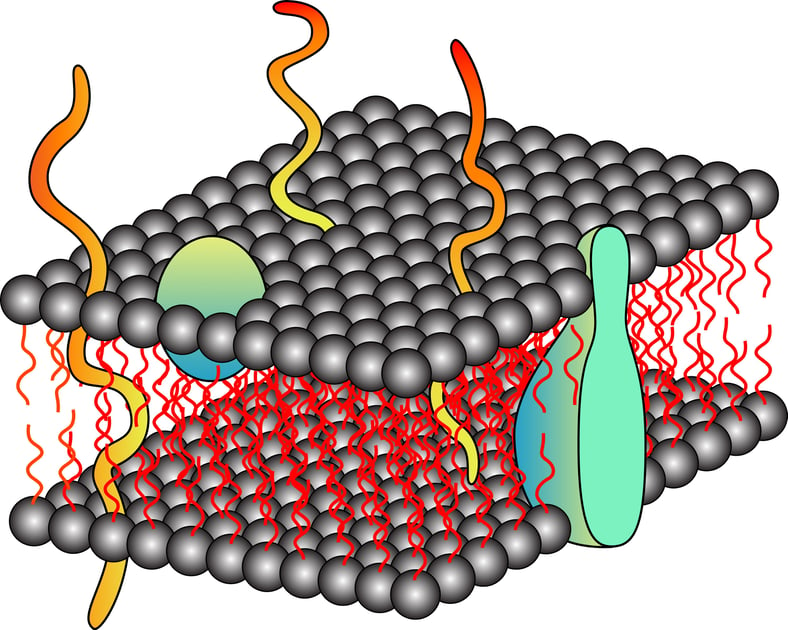
Proteins are the building blocks of cells and are the most abundant and diverse biomolecules. Proteins are literally responsible for almost all the functional aspect of a cell, from making the cellular membrane to catalyzing a biological reaction. As per the database, approximately 20-30% of the total encoded proteins have integral membrane proteins while 10-20% portion comprises membrane-associated proteins. This diverse group of proteins includes signal transducers, transporters, membrane channels, and cell surface receptors. This specialized group of proteins has become a target for therapeutic drug development in the past few decades. However, due to the unavailability of complete structural details of these proteins, targeting is a little difficult and that makes drug designing trickier than expected. The right approach is to design polished methods that can help the extraction of membrane proteins and their analysis.
Topics: Protein Purification, Detergents, Protein Extraction
A Tutorial for 3D Cell Culture System: Bridging the Gap between in-vitro and in-vivo cultures
Culturing cells in the dishes has been the most critical and an important tool in the field of drug discovery and development for decades. Cell culture based assays allow a simple yet cost-effective technique bypassing tedious and tiresome animal-testing. This also provides a controlled situation, which can provide results based on the responses of chosen cells due to any stimuli or drug. For the past few decades, many of the methods were developed keeping the conventional two-dimensional monolayer culture in consideration where a single layer of cells is grown on a flat surface having a matrix on it. Nonetheless, 2D culture came as a boon for cell-based assays, but it did have its own share of limitations. The most important of all is the inadequate consideration of in-vivo environment where the cells are surrounded by the extracellular membrane in a 3-dimensional manner while 2D cultures do not consider cell-cell interaction in a 3D fashion providing an incoherent data.
Molecular biology based diagnostics are gaining wide importance for detecting diseases. Molecular diagnostic kits are simple and can either be used by a professional healthcare personnel or by the patient at home. Point of care diagnosis is gaining importance as it is easy to use in remote places by individuals with less or no experience without the need of sophisticated equipment. This method is based on techniques like PCR, in situ hybridization, ELISA, etc., that detect biomarkers specific for that particular disease. Lateral flow assay is one of the point of care techniques used to detect human, animal and plant diseases, food testing or soil testing. Usually liquid samples like blood, urine, serum, milk etc., are suitable for testing by this method but solid sample like tissues, soil, food etc., can also be tested by mixing the samples in suitable buffers.