Molecular biology based diagnostics are gaining wide importance for detecting diseases. Molecular diagnostic kits are simple and can either be used by a professional healthcare personnel or by the patient at home. Point of care diagnosis is gaining importance as it is easy to use in remote places by individuals with less or no experience without the need of sophisticated equipment. This method is based on techniques like PCR, in situ hybridization, ELISA, etc., that detect biomarkers specific for that particular disease. Lateral flow assay is one of the point of care techniques used to detect human, animal and plant diseases, food testing or soil testing. Usually liquid samples like blood, urine, serum, milk etc., are suitable for testing by this method but solid sample like tissues, soil, food etc., can also be tested by mixing the samples in suitable buffers.
Lateral flow assay can be developed either by sandwich method (color develops for positive test) or competitive method (color disappears for positive assay). The first component of a lateral flow device is sample pad that contain a filter to distribute sample evenly. Sample to be tested is added to this sample pad. Second component is the conjugate pad that contain conjugated antibodies or antigens that binds and moves with target present in the sample. Conjugate pad can be made using gold, latex, carbon nano particles, magnetic beads or colored polystyrene beads. The next component is a nitrocellulose membrane where binding reagents (antigen or antibody) binds the target with conjugate and develops color line representing a positive test.
The result can be quantified using specific reader device as well. Finally the excess sample is absorbed by an absorbent pad.
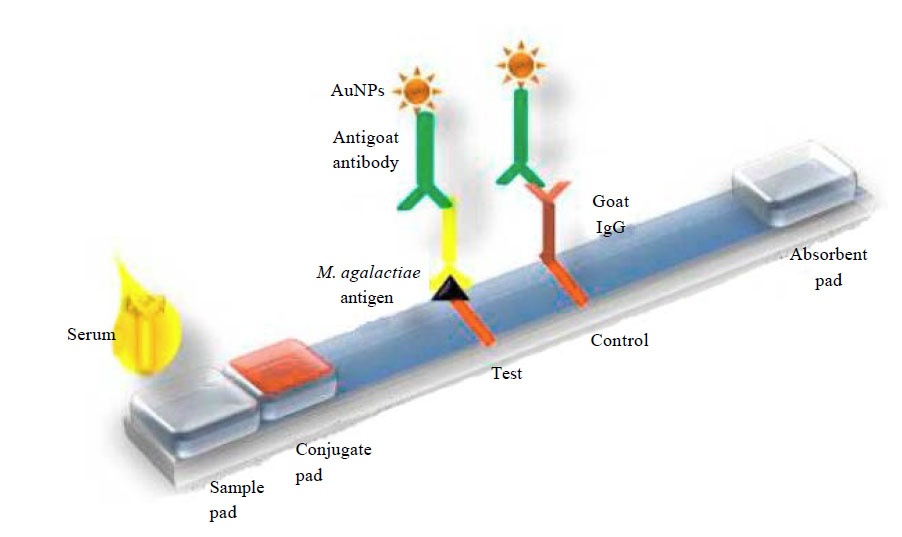
Pictoral representation of Lateral flow device adapted from Arun et al, 2014.
Method: Specific antibodies will be raised against the antigen and these specific antibodies will be conjugated to nanoparticles (gold nanoparticles are widely used) and immobilized on conjugate pad. Antigen in the sample binds to this conjugate, this complex (antigen+ antibody+nanoparticle) mobilizes along the membrane and binds to specific antibodies at the test line and color is visible due to the nanoparticles. The unbound conjugate move further and bound to antibody at control line which will be visible in both negative and positive cases.
Advantages: The results can be obtained with in 5-10 min hence useful for point-of- care diagnosis. Hand held lateral flow readers or photometers can be used to get quantitative results.
Drawbacks: Though certain products based on lateral flow assay can be quantitated to some extent, most of them are for preliminary diagnosis. To confirm the results, one have to test the samples by PCR or other quantitative assays.
Some Examples:
After the development of this technique by Unipath in late 80s, the concept was popularised and adapted by hundreds of companies to develop kits for application in clinical, veterinary, food and beverage, environment, water testing, Pharma and biologics.
- Human Pregnancy test, detection of HCG is widely
- Diagnosis of canine infections caused by Parvovirus, Corona virus, Rabies virus ,
- Diagnosis of Brucella, TB etc., in
- Avian Influenza tests in
- Aflatoxin B1 in cattle and poultry
- Detection of biomarkers like Albumin for diabetes, Lipoprotein-A for Atherosclerosis, PAPP-A for Acute coronary syndromes ,
Though there are many diagnostic kits developed so far, there is a need for more accurate and simpler techniques to be developed for other diseases also.
References:
- T.R. Arun, R. Rana, P. Singh, P. Choudhuri, V.P. Singh, P. Thomas, V. Rekha, K. Nehra, J. Usharani and K. Dhama, 2014. Development of a Gold Nanoparticle Based Lateral Flow Assay for Rapid Diagnosis of Contagious Agalactia in Goats. Asian Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances, 9: 405-413.