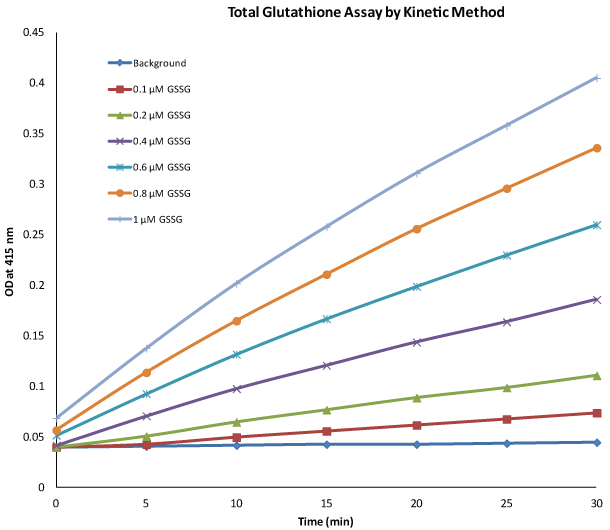
Monitor oxidative stress to determine the extent of cell damage using a colorimetric gluthathione assay.
Topics: Cytotoxicity Assays
The Advantages of Loading Controls in Western Blotting
Loading controls serve as a vital method of verifying the results acquired through western blotting. Loading controls are antibodies that are used to detect proteins within samples. When western blots are used to determine the levels of protein expression in a sample, loading controls ensure that the results aren't due to loading or protein transfer errors. When using a loading control, the right type of control must first be identified.
Tips for Preventing a High Background During Western Blotting
A high background is one of the most common quality control issues encountered during the process of western blotting. When a high background occurs, it can be very difficult to distinguish the relevant data from the irrelevant data. A uniform high background can be caused by numerous issues and may take some work to resolve -- but without resolving the situation, the blot may not be readable.
DNA denaturation is the process of breaking down the DNA molecule, generally for the purposes of comparison or sequencing. As with many laboratory techniques, there are a variety of ways to denature DNA -- and each of them tend to be better for specific applications. The top three methods of DNA denaturation are heat, NaOH treatment, and salt. Each of these methods will break the bonds between strands, but may do so with a greater degree of accuracy or lessened disruption.