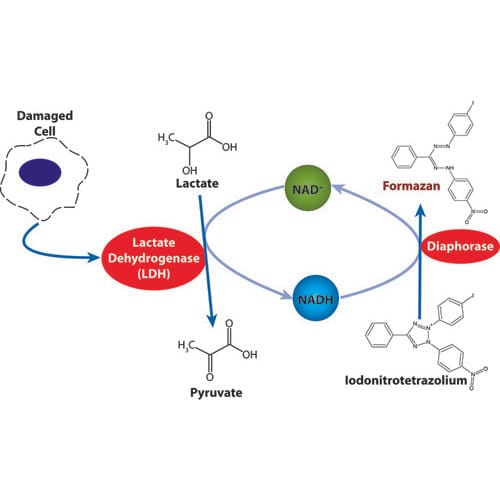
A reliable LDH cytotoxicity assay detects cell toxicity, cell death, cell viability, and cell proliferation. It is also ideal for the application of cell-free supernatants from cells in culture (adherent or suspension).
What should you consider when selecting a protein extraction buffer?
Proteomes can be made up of more 15,000-20,000 different protein species that differ greatly in properties such as molecular mass, charge, abundance, hydrophobicity and other characteristics. Extraction of proteome for analysis is therefore a daunting task that requires careful attention to details. Sample preparation for proteome analysis requires solubilization of proteins. The choice of optimal method for solubilization of protein mixture is critical since sample preparation affects the outcome of analysis. Usually the steps involved are homogenization, solubilization and stabilization when proteome sample is prepared from cells or tissues.
Topics: Protein Extraction
Plasmid Isolation: Overcoming the Challenges for Isolating Plasmid DNA
Plasmid isolation is crucial to biology and an essential step in various procedures, including cloning, DNA sequencing, transfection, in vitro translation, blotting, and gene therapy. However, these applications require the isolation of high-purity plasmid DNA. Whereas genomic DNA extraction is simple and straightforward, plasmid DNA extraction can be more complicated.
Topics: Molecular Biology
Taq Polymerase is Preferred Enzyme for Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A DNA Polymerase is a vital biological enzyme that is present in DNA replication. In the process, DNA copies into two daughter DNA molecules and synthesizes a new DNA strand from the existing strand by adding dNTPs to the growing DNA.
Topics: Molecular Biology