Biotechnology is the fastest growing occupation among industries, expected to grow 11% by 2022. Teaching biotechnology through the applications of biology, chemistry, engineering research, and manufacturing techniques is critical to the future of creating products and services that improve the quality of human life.
The Protein Man

Recent Posts
The stability of proteins is crucial in many in vitro protein studies and is considered a major requirement in functional studies involving native and recombinant proteins. Thus, understanding protein stability and preserving the native conformation and normal functions of your protein of interest can be very helpful when working with your protein of interest.
Topics: Protein Purification, Protein Extraction
The Advantages of Using Trypsin for Mass Spectrometry
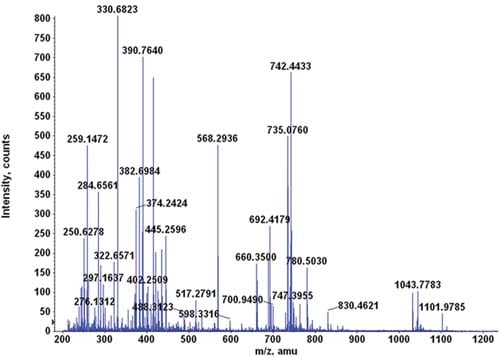
In mass spectrometry-based proteomics, nothing comes close to trypsin in breaking down protein mixtures into peptide fragments. In fact, protein researchers consider trypsin as the runaway winner when it comes to protease activity and specificity – and there are a lot of good reasons why they do.
Topics: Mass Spectrometry
When it comes to labeling your antibodies for downstream application requiring signal detection, you have two choices. You can either go for the direct approach or the indirect approach. How do you know which method to use? Here are some things you need to know to make sure you pick the right method for the intended application.
Topics: Antibody Production, Protein Labeling

.jpg?width=788&name=Protein%20Structure%20(8).jpg)