Protein cross-linking reagents, fondly called “cross-linkers” by researchers, are molecules with two or more reactive ends that can attach themselves to specific functional groups (e.g., primary amines, carboxyls, sulfhydryls, carbohydrates, and carboxylic acids) on proteins and other biomolecules via a covalent bond.
8 Factors to Consider when Selecting a Protein Cross-linker
Topics: Cross-Linkers
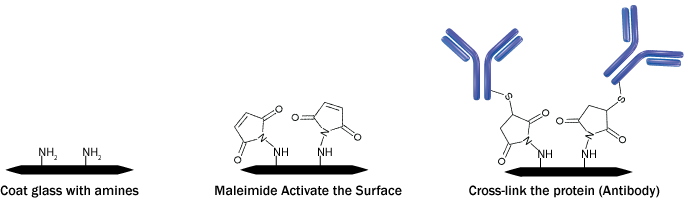
Study Protein to Protein Interaction with Protein Cross Linking to Glass
In all the complex biological processes, the mechanism underlies a synchronized and orchestrated molecular organization, which works through protein-protein interactions. These interactions could be transient, such as catalytic or signal-transduction pathways, requiring a transitory protein-protein association. Alternatively, stable or semi-stable multi-protein complexes are also formed in many biological functions. Hence, in order to identify transient and semi-stable protein associations, chemical cross-linking of proteins came as a useful technique. It involves the formation of chemical covalent bonds between the interacting protein utilizing bifunctional reagents consisting of reactive end groups, which can react with the functional groups of amino acid residues, such as primary amines and sulfhydryls. The formation of cross-links provides direct and concrete information regarding the identity of the interacting proteins as well as the regions of contact between the proteins.
Topics: Cross-Linkers
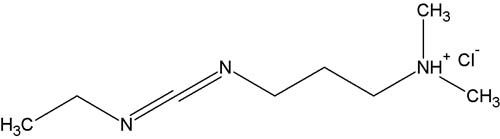
High Efficiency & Stability Protein CrossLinking with EDC & NHS
EDC is the most popular zero-length crosslinker for biochemical conjugations because it can efficiently form conjugates between two protein molecules, between a protein and a peptide, and between proteins and oligonucleotides, and with small molecules.
Topics: Cross-Linkers
Modifying Oligonucleotide 5'-Phosphates By EDC for Improved Coupling
The heterobifunctional, zero-length carbodiimide crosslinker EDC is a versatile tool that can be used with Imidazole to modify, label, immobilize or bioconjugate oligonucleotides, DNA and RNA at their 5’ phosphate groups for a variety of applications:
Topics: Cross-Linkers