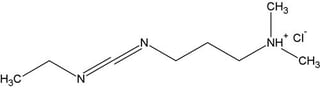
The heterobifunctional, zero-length carbodiimide crosslinker EDC is a versatile tool that can be used with Imidazole to modify, label, immobilize or bioconjugate oligonucleotides, DNA and RNA at their 5’ phosphate groups for a variety of applications:
- Conjugate carboxyl to amine groups in peptides and proteins
- Oligonucleotide/DNA/RNA labeling through 5’-phosphate groups
- Couple haptens or peptides to carrier proteins
- Immobilize peptides for affinity purification
- Crosslink proteins to carboxyl surfaces and beads
- Convert carboxyls to amine-reactive Sulfo-NHS esters
- Activate nanoparticles to amine-reactive Sulfo-NHS esters
This blog focus on the use of EDC in the modification of 5'-phosphate groups of oligonucleotides.
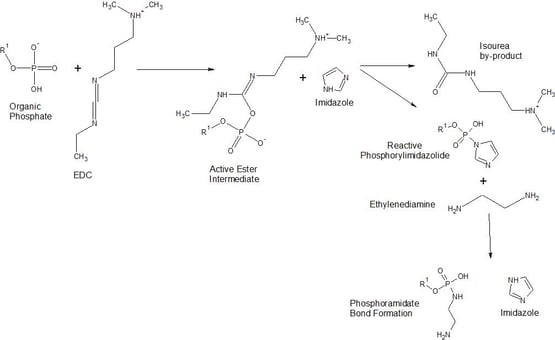
Oligonucleotides containing a 5’-phosphate group can be reacted with EDC and imidazole to create nucleotide phosphoramidate conjugates. The incorporation of Imidazole with EDC provides better reactivity toward amine nucleophiles and increases derivatization yield over carbodiimide only reactions. First, EDC rapidly reacts with phosphates or carboxylates to form an active complex able to couple with primary amine-containing compounds. The carbodiimide activates an alkyl phosphate group to a highly reactive phosphodiester intermediate. Then Imidazole reacts with the phosphomonoester at the 5’-terminus of DNA to form a highly reactive phosphorimidazolide. A reactive phosphorimidazolide will rapidly couple to amine-containing molecules (diamine spacer molecules or amine containing probes) to form a phosphoramidate bond.
Modifying Oligonucleotide 5’-Phosphate Groups Protocol
Materials Required
- EDC (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino) propyl carbodiimide, hydrochloride)
- Ethylenediamine or orther amine or hydrazide-containing molecule
- 0.1 M Imidazole, pH 6
- Reaction Buffer, such as phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with EDTA: 10 mM sodium phosphate, 0.15M NaCl, 10mM EDTA, pH7.2.
NOTE: Avoid using PBS with > 10mM phosphate, which will interfere with the intended reaction. Other amine-free and carboxylate-free buffers may be substituted, but avoid Tris, which contains primary amine that will quench the reaction. - 7.5-15 nmol (~60-120 µg) oligonucleotide or double-stranded DNA or RNA dissolved in ~10 µl Reaction Buffer.
Protocol
- Dissolve ethylenediamine (or alternative) to a final concentration of 0.25M in 10µl of 0.1M imidazole.
- Weigh 1.25mg (6.52µmol) of EDC into a microcentrifuge tube.
- Add 7.5µl of the prepared oligonucleotide to the tube containing the EDC and immediately add 5µl of the ethylenediamine/imidazole solution.
- Vortex tube until contents are completely dissolved and then briefly centrifuge the tube to gather contents.
- Add an additional 20µl of 0.1M imidazole, pH 6.
- Incubate reaction at one of the following conditions:
50°C for 30 minutes to 2 hours
37°C for 1 hour to overnight
Room temperature for 2 hours to overnight - Remove non-reacted EDC and its by-products and imidazole by dialysis or spin desalting column using 10mM sodium phosphate, 0.15M NaCl, 10mM EDTA, pH 7.2, or other suitable buffer.
NOTE: The amine-modified oligonucleotide may be stored frozen for up to one year or used immediately for other conjugation reactions. If heterobifunctional hydrazide compounds were used, purify and store the conjugate in a manner suitable for stability of the second reactive group.
Other related blog titles:
- How To Determine Degree of Protein Labeling
- Biotin Labeling: Key Points to Selecting Your Biotin Agent