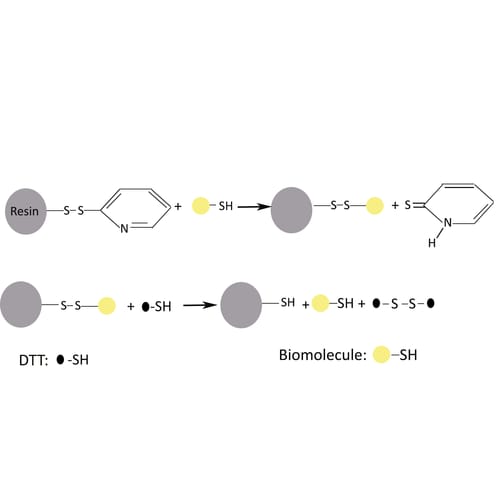
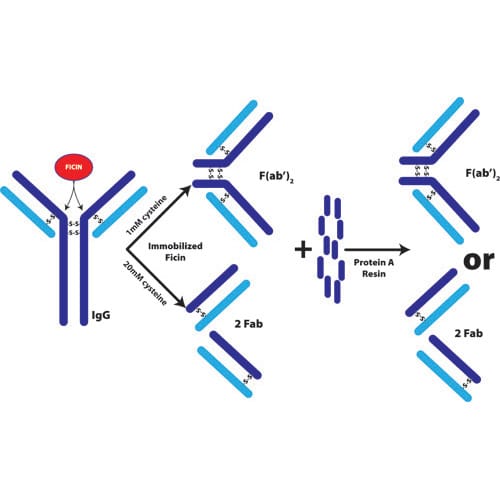
Ion Exchange Chromatography Resins and Methods
Topics: Resins
Affinity purification (also called affinity chromatography) is recognized as the most powerful method of purification chromatography or enriching a protein of interest from a complex mixture such as a crude cell lysate, cell culture supernatant, or other samples.
Affinity purification (also called affinity chromatography) is recognized as the most powerful method of purification chromatography or enriching a protein of interest from a complex mixture such as a crude cell lysate, cell culture supernatant, or other samples.
What Are Monoclonal Antibodies, and How Are They Made?
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs or MoAbs) are immune system proteins that were discovered in 1975 as a highly specific targeted molecule - it will bind to its target molecules with high specificity. It could take a load of drug or agent and deliver it to the target. Because of its specificity, monoclonal antibodies have found its use in medical science to treat a wide variety of diseases, including some types of cancer, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Crohn’s disease, and psoriasis, and minimize or eliminate the risk of transplant rejection.
Topics: Antibody Production