Assessing Nucleic Acid Purity Via Absorption Spectroscopy
Assessing Nucleic Acid Purity Via Absorption Spectroscopy
Posted by
The Protein Man on Sep 14, 2023 1:38:32 PM
0 Comments Click here to read/write comments
Read More
0 Comments Click here to read/write comments
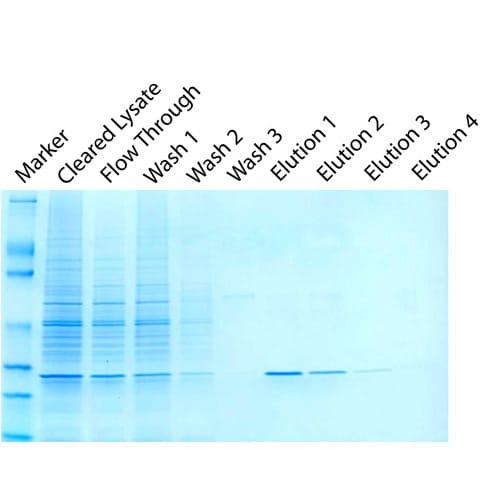
A DNA ladder, also known as a molecular size marker or standard DNA marker, is a solution containing DNA fragments of varying lengths and sizes that serves as a reference in estimating the size of unknown DNA molecules after they are separated by agarose or acrylamide gel electrophoresis. DNA ladders are the mainstay in every laboratory that routinely performs DNA experiments.
0 Comments Click here to read/write comments
Topics: Molecular Biology