How do you know which method to use for visualizing proteins after immunodetection? Should you be using the direct detection method or would applying an indirect detection method best serve your purpose? If you’re not sure which method to use, here are some things you definitely need to know.
When to Use Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Detection vs. a Direct Method
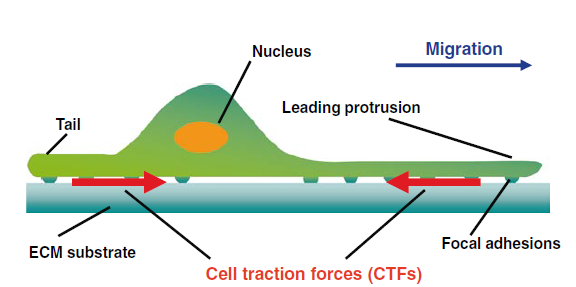
Traction Force Microscopy for cell interaction with extracellular matrix
The fundamental source of all processes in living system is force. Force is required to maintain the balance between the external and internal environment of any living system. Cells have the ability to sense and respond to the forces. Cells perform different activities such as migration and interaction with extracellular ligand. While performing all these vital functions required of normal development and maintenance of homeostasis, cells perform a myriad of feedback mechanisms in order to adjust with the mechanics to correlate with the physiological needs of the cell. Hence, in a nutshell, cells have a dynamic reciprocation of exertion and resistance force to tune with the material properties of the extracellular matrix and help to assert physical interactive forces with the neighboring cells or with the extracellular milieu. Consequently, it is essential to measure these cellular forces to understand different functions and properties of the cell. Cellular forces are not evenly distributed in space and vary according to the substrate. When cells are cultivated on a specific substrate, especially when grown in-vitro, the forces, also known as cell traction forces, are exerted by the cells at localized regions known as focal adhesion sites which is subsequently attributed to the physical properties of the cell and the substrate interaction.
Topics: Teaching Biotechnology
Immunoprecipitation Protocol: Critical Parameters
- Antigen extraction: As mentioned in the general protocol, cellular antigens are required to be extracted from a suitable source depending on the experimental requirement. The extracting method should be able to make antigens accessible for binding with the specific antibody. The antigens should be in a physical form in order to allow its separation from other cellular components. Hence, extraction with nondenaturing detergents such as Triton X-100, Nonidet P-40, CHAPS, digitonin, or octyl glucoside can allow the exposure of epitopes in the antigen for better binding with antibodies. Some of these detergents can even preserve weak protein-protein interactions, for example, digitonin. Some antigens are insoluble in non-denaturing detergents such as cytoskeletal structures, chromatin, membrane “rafts” or the epitope is hidden between the folded motifs of the proteins, and in that condition it is preferred to extract the antigens under denaturing conditions.
- Antigen Concentration: The cellular abundance of the immunoprecipitated antigen is essential to determine efficiency of immunoprecipitation. Radio labelling or non-radiolabelled methods are suitable to detect antigens as low as 10,000 to 100,000 copies per cell, which is generally the case with signal transduction proteins, transcription factors or endogenous integral membrane proteins.
- Pre-Clearing of the protein sample: In order to start immunoprecipitation, pre-clearing of the antigen sample is an additional step. The samples are incubated with the beads (Protein A and G or A/G) in order to get rid of unwanted antigens. The non-specific antigens get bound with the solid phase and hence can be removed by low-speed ultracentrifugation.
- Antibody purification method: Polyclonal antibodies used for IP could be in the form of whole serum, ammonium sulphate–precipitated immunoglobulin fractions, or affinity-purified immunoglobulins. Among all these, affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies are preferred as they are relatively specific and give lesser background.
- Antibody selection- Polyclonal versus monoclonal: The selection of type of antibody most suitable for IP is most important, though it is not an easy way.
| Type of Antibody | Pros | Cons |
| Polyclonal antibodies |
|
|
| Monoclonal antibodies |
|
|
Hence, an informed empirical approach should be used to choose the antibody to get satisfied results.
- Antibody titer: The titration of the antibody is required to get an optimal result. Too less of antibody will give inefficient immunoprecipitation while too much of antibody can create nonspecific IP because of increased amount of immunoglobulins bound with the beads.
- Immunoadsorbents: Immobilized proteins (protein A, G, A/G and recombinant proteins) are efficient for antibody adsorbent and provide a beaded support. Click here for a comparison of these immobilized proteins in terms of Immunoglobulin binding.
Both Protein A and protein G are relatively stable and can be sedimented easily by low -speed centrifugation. Although, some polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies may not efficiently bind with all protein A or protein G, which can be solved by using an intermediate antibody to the immunoglobulin of interest. - Nonspecific controls: For correct interpretation of the result, it is critical to include appropriate controls for any experiment. For Immunoprecipitation, appropriate nonspecific controls with the specific samples are used. Generally two types of controls are used:
- Incubation of an irrelevant antibody similar to the experimental antibody which share biochemical similarity and belong to same species and immunoglobulin subclass. "No antibody" controls are strongly not advised.
- Perform an Immunoprecipitation from the cells/tissues that do not express a specific antigen along with an immunoprecipitation of the antigen-expressing samples.
- Washing: The washing steps must be optimized for sufficient removal of unbound proteins. Additional washes are most likely to reduce antigen-antibody association while insufficient washes may lead to background. The last PBS wash is required to remove detergent from the complex which might reduce the resolution on SDS-PAGE and other components of the buffer.
- Analysis of Immunoprecipitation result: The immunoprecipitated antigens can be analysed by different ways such as Western blotting, ELISA and mass spectrometry.
Related Blog Posts
Topics: Protein Purification
The cardinal principle behind immunoprecipitation (IP) is the isolation of an antigen by interaction between the antigen and a specific antibody conjugated to a sedimentable matrix. Antigen source may vary from cells or tissues without labeling, radio labeled or tagged cells, labeled or unlabeled proteins isolated from subcellular fractionation or in-vitro translated proteins. Immunoprecipitation can also be helpful in protein fraction analysis separated by gel filtration or differential sedimentation based on density gradients. In order to capture interacting antigens, antibodies developed from various animal species that could be either polyclonal or monoclonal, are used for immunoprecipitation. These antibodies are tagged non-covalently with specific immunoadsorbents such as protein A–or protein G–agarose or covalently linked with a solid-phase matrix.
Topics: Protein Purification