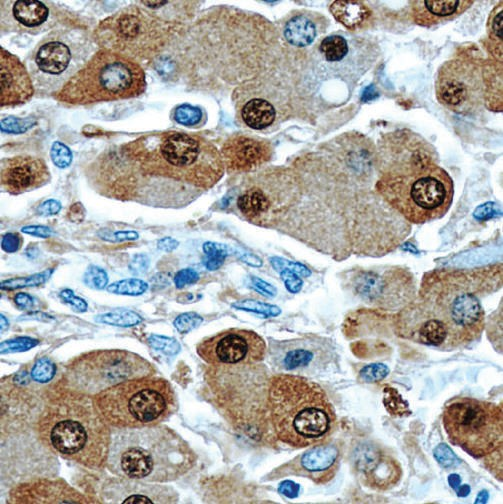
Aside from tissue biopsy, cytology serves as an indispensable tool in screening and diagnosing cancer. In this technique, a cytological material is obtained from the patient, spread onto glass slides for microscopic examination, stained, screened for abnormalities and assessed prior to the issuance of a final report. Cytology differs from histology in that the sample usually consists of a suspension of cells whereas histology samples are usually sections of actual tissue. For example; a Gill’s hematoxylin single strength formulation would be much better suited for cytology, whereas a triple strength formulation would be better for tissue sections.
Topics: Cytotoxicity Assays
Tetrazolium reduction assays are characterized by reduction of various tetrazolium analogs (MTT, MTS, XTT, WST-1, and INT) and quantification of the subsequent color change. The MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay was originally developed as an alternative to the radioactive thymidine incorporation assay. It was one of the first assays to be developed for the 96-well plate format intended for high throughput screening in 1983 by Tim Mossman. The MTT assay differs slightly from the radioactive thymine incorporation assay as the MTT assay measures the cell viability of a solution as opposed to cell proliferation. This assay is therefore is an incredibly useful tool in determining drug cytotoxicity or differentiating between multiple cell lines.
Topics: Cytotoxicity Assays
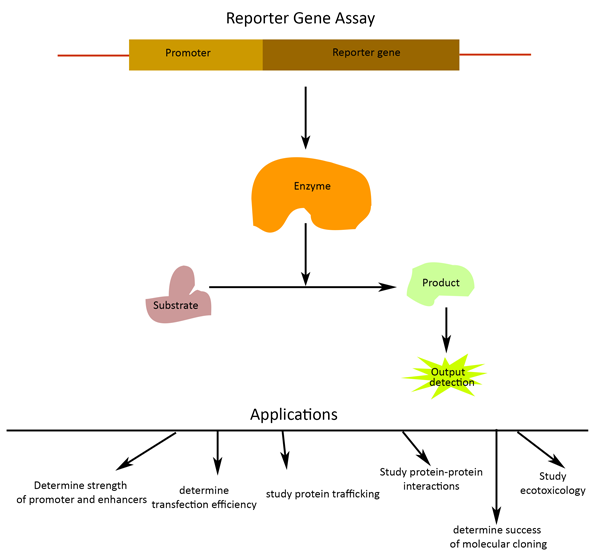
Role of reporter genes to assay for transcription factors & more
Reporter Gene Assays and their applications
Reporter gene assays are paramount for study of regulation of gene expression by gene regulatory elements (cis-acting factors), transcription factors or exogenous regulators (trans-acting factors). In reporter gene assays, the activity of a reporter gene is measured. A reporter gene is joined to a target regulatory DNA sequence in an expression vector, which is then transfected into the cell type of choice. The reporter gene is transcribed and translated in the cells and its activity is measured to access the strength or function of the target regulatory DNA sequence or study effects of transcription factors or potential drugs etc.
Topics: Cytotoxicity Assays
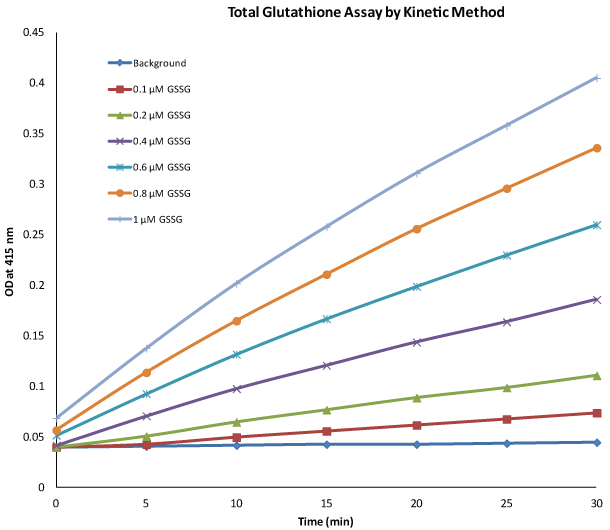
Monitor oxidative stress to determine the extent of cell damage using a colorimetric gluthathione assay.
Topics: Cytotoxicity Assays