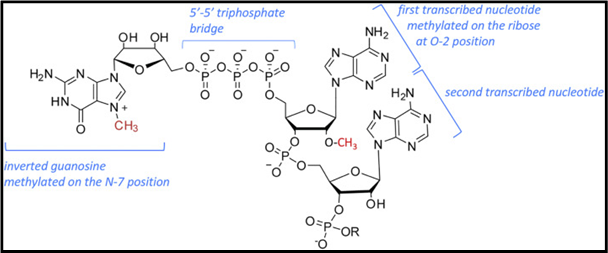
Regulating the Cell Cycle
What Are Biocides?
Biocides are non-antibiotic agents used as preservatives, disinfectants, or antiseptics. Although most biocides are chemical agents, microorganisms can also be used as biocides to suppress the growth of other organisms. Biocides act either by killing microorganisms or inhibiting their growth. Biocides can be further classified by their intended application. Preservatives are added to products to increase their shelf-life by preventing microbial decomposition. Disinfectants are agents that are applied to inanimate objects and surfaces, whereas antiseptics are agents applied to living tissue such as mucous membrane or skin. In today’s world, biocides are frequently encountered. Preservatives are ubiquitous and are found in a diverse array of products ranging from food, beverages, and cosmetics to pharmaceutical drugs, biological samples, and research products. Likewise, the use of disinfectants has increased dramatically in response to the worldwide pandemic, and antiseptics are increasingly important in hospital settings.
Topics: Molecular Biology
DNA and mRNA Vaccines: A Side-by-Side Comparison
What’s the difference between DNA and mRNA vaccines and how do they work? Are they better than traditional vaccines? With all the exciting life-saving possibilities these modern technologies offer, it’s time to take a closer look.
Topics: Molecular Biology
In eukaryotic cells, RNA processing occurs in the nucleus and the functional mRNA is transported to the cytoplasm. As soon as the mRNA transcript is synthesized from RNA polymerase II, RNA binding proteins (RBPs) attach to the mRNA transcript to prevent it from degradation during processing and exporting it from the nucleus. RBPs play an important role in RNA stability, maturation, transport, and localization. This process results in the formation of stable mature mRNA (lasts for several hours) than that in prokaryotes (5 seconds).
Topics: Molecular Biology

.jpg?width=788&name=G-Biocide-500x500%20(1).jpg)