The Protein Man

Recent Posts
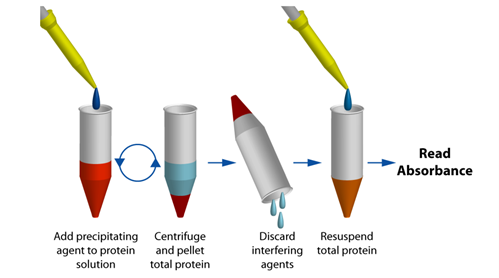
Protein Quantitation in the Presence of Reducing Agents and Detergents with UPPA™
Posted by
The Protein Man on Jul 14, 2021 1:00:00 PM
0 Comments Click here to read/write comments
Topics: Protein Purification
Pollution poses a real threat, not only to the environment but to our very existence as well. Aside from poisoning our soil, waterways, and the air we breathe, pollution also causes considerable damage to plant, animal, and human lives and imperils the sustainability of our planet.
0 Comments Click here to read/write comments
Read More
0 Comments Click here to read/write comments
Read More
0 Comments Click here to read/write comments