The availability of purified antibodies is essential to various applications. While there are various methods of purification, affinity chromatography is the most popular antibody purification technique.
Affinity chromatography offers high selectivity and involves minimal steps to provide simplicity. It also implements an effective protocol that typically requires extensive planning and testing to achieve high purity.
What is Affinity Chromatography?
Affinity chromatography is a laboratory technique that purifies proteins or protein complexes within a biochemical mixture. It relies on the reversible interaction between a protein and a specific ligand immobilized in a chromatographic matrix.
Unlike other methods of purification, such as gel filtration or size-exclusion chromatography, affinity chromatography manipulates specific molecular properties and binding interactions between molecules to purify the protein of interest.
In affinity chromatography, a particular ligand chemically immobilizes to a solid support, so the molecules with specific binding affinity bind to the ligand after a complex mixture passes over the column.
While other sample components wash away, the bound molecule separates from the support and results in purification from the original sample.
What is Antibody Purification?
Antibody purification is the selective enrichment or specific isolation of antibodies from serum (polyclonal antibodies), ascites fluid, or cell culture supernatant of hybridoma cell line (monoclonal antibodies).
How Does Antibody Purification by Affinity Chromatography Work?
Affinity chromatography is the only technique that enables the purification of biomolecules on the basis of its biological function or individual chemical structure. It relies on the reversible interaction between a protein and a specific ligand.
It is based on the high affinity and specificity of Protein A and Protein G for the Fc-region of lgC from various species. The binding of an antibody to the ligand is reversible, and the antibody is eluted by lowering the pH.
In affinity chromatography, the sample is applied under conditions that favor specific binding to the ligand as a result of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. After washing away the unbound material, the bound protein is recovered by changing the buffer conditions, resulting in its purification from the original sample.
Antibody Purification Resins
At G-Biosciences, we offer a wide selection of reagents for the purification of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, including Immobilized Protein A and Immobilized Protein G. These resins bind the constant domains of the protein allowing for the enrichment of all antibodies from the starting serum or ascites.
Immobilized Protein A
Immobilized Protein A allows for the consistent binding of constant domains of immunoglobulin (lg) molecules. Protein A is coupled to agarose beads by reductive animation method that provides high coupling efficiency for immunoglobulins and minimal protein A leaching (<5ng protein A/ml). Immobilized Protein A has a high binding capacity (>40mg human IgG/ml resin).
Immobilized Protein G
Immobilized Protein G enables the one-step purification of classes, subclasses, and fragments of immunoglobulin (lg) molecules for biological fluids and cell culture media. It also binds the constant domains of immunoglobulin molecules.
As a modified form of Streptococcal group G, Protein G does not bind to albumin. It is coupled to 4% highly cross-linked agarose beads by a proprietary coupling method that provides high coupling efficiency for lg and minimal protein G leaching. Immobilized Protein G has a high-binding capacity (>20mg sheep lgG/ml resin).
Protein G can be used for the purification of mammalian monoclonal and polyclonal IgGs that do not bind well to Protein A. Immobilized Protein G has a greater affinity than Protein A for most mammalian IgGs, particularly for certain subclasses, including human lgG3, mouse IgG1, and rat IgG2a.
Affinity Chromatography is used for purification of specific antibodies. As stated previously, a ligand, specific for the antibody of interest, needs to be covalently immobilized to a solid support, such as agarose beads. G-Biosciences offers several resins for the immobilization of ligands and the choice is determined by:
- The residues that can be used on the ligand for conjugation
- The coupling chemistry
For coupling through primary amines
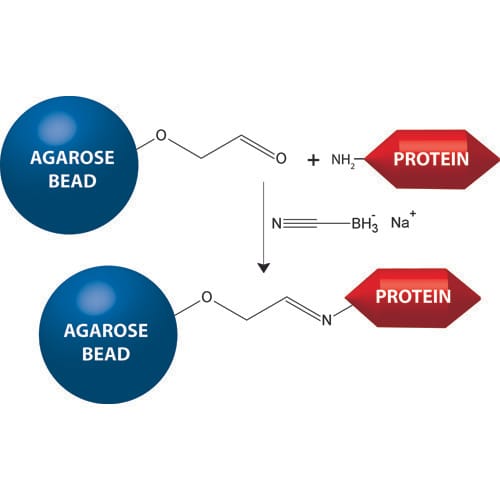
- Aldehyde Activated Agarose: Uses reductive amination of Schiff base complexes
- CDI Amine Reactive Agarose: Uses reactive imidazole carbamates. Ideal for ligands in solvents
- NHS-Activated Agarose: Uses a a reactive NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide) group
- CNBr-Activated Agarose: Cyanate esters react with primary amine ligands
- ECH-Agarose: Immobilized carboxyls form covalent bonds through a protein crosslinker (EDC)
- Epoxy-Activated Agarose: Immobilized epoxy groups react with amines, carboxyls, sulfhydryls and hydroxls to form covalent linkages
For coupling through carboxyl groups
- Immobilized DADPA (Diaminodipropylamine): Consists of a free primary amine that can be conjugated to carboxyls with the heterobifunctional crosslinker, EDC.
- Epoxy-Activated Agarose: Immobilized epoxy groups react with amines, carboxyls, sulfhydryls and hydroxls to form covalent linkages
For coupling through sulfhydryl groups
- Sulfhydryl Coupling Resin (Iodoacetyl Resin): Immobilized iodoacetyl groups specifically react with free sulfhydryls to form covalent, permanent thioether bonds
- Epoxy-Activated Agarose: Immobilized epoxy groups react with amines, carboxyls, sulfhydryls and hydroxls to form covalent linkages
For coupling through carbohydrate groups
- Carbohydrate Coupling Resin (Hydrazide Resin): The immobilized hydrazide group reacts with oxidized carbohydrates to form covalent hydrazone bonds.
G-Biosciences is Your Destination for Antibody Purification Essentials
G-Biosciences has the equipment you need for successful antibody purification by affinity chromatography. To shop our selection of products, visit our website today!