Question
I am looking to isolate proteins stuck to membranes in human and animal brain. I am then running the protein I retrieve on 2D gels. At the moment I am using a crude method to retrieve these proteins. This method is very time consuming and lacks reproducibility.
Do you have advice for isolating membrane proteins as well as aggregated protein stuck to the membrane for their subsequent analysis by 2D protein electrophoresis? Can I resuspend the proteins straight into my buffer for rehydration and IEF?
The Protein Man Says:
Purification of membrane proteins from tissues is a relatively easy process, but is definitely complicated when the downstream analysis is 2D electrophoresis. Routinely used detergents, metal chelators and reducing agents effect protein resolution on 2D gel electrophoresis resulting in poor or artifactual results.
Routine isolation of membrane proteins normally involves the time consuming isolation of membranes using gradient separation and expensive ultracentrifugation equipment. Even after this laborious process is complete the resulting membranes and their proteins may not be suitable for 2D electrophoresis.
The Protein Man recommends our line of FOCUS products that are fully compatible with 2D electrophoresis.
CLICK HERE FOR A COMPETE GUIDE TO OUR FOCUS PRODUCTS
FOCUS Membrane Protein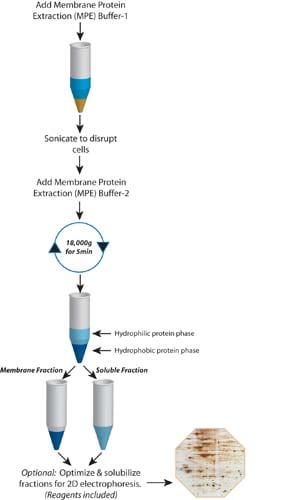
A product specifically designed for a simple, rapid and highly reproducible method for preparation of membrane or hydrophobic proteins from biological samples for 2D-gel analysis or other applications. This kit does not require the use of difficult to prepare gradients or the use of expensive ultracentrifuge equipments. Click for further details
Is it compatible with 2D protein electrophoresis?
Yes, the kit is supplied with a unique precipitation product that allows for 100% protein recovery and the removal of all agents that interfere with 2D electrophoresis.
How to isolate proteins associated with membranes?
Integral membrane proteins are relatively simple to isolate as they are separated out with the membranes. Peripheral membrane proteins are harder to isolate as they are not embedded in the membrane and can readily disassociate during membrane fractionation. A simple solution is to covalently couple the loosely associated peripheral proteins to the embedded integral proteins. A routinely used technique is to treat samples with a short protein cross-linker that will chemically link peripheral proteins to the integral membrane proteins. This allows for their fractionation in the membrane fraction and subsequent analysis. To analyze peripheral proteins on the inside of the cell use a membrane permeable cross-linker, to analyze external membrane associated proteins, such as ligands, use a membrane impermeable cross-linker.
To reverse the cross linking it is advisable to use a cross-linker with a disulfide bond that can be reduced and break the cross-linker.
There are a large number of cross-linkers available.
CLICK HERE FOR A COMPETE GUIDE TO PROTEIN CROSS-LINKERS
The Protein Man Review
- Fractionate membranes using method of choice, or a commercially available product.
- Perform a crucial 2D clean up before 2D electrophoresis
- For peripheral proteins, explore the use of a protein cross-linker